|
|||||
|
Concrete General Properties
| |
|
Name
|
Material name
|
|
Type
|
Concrete
|
|
ν
|
Poisson ratio (
Default value depends on the active code:
ν = 0.2 Eurocode 2 (Art 3.1.2.5.3)
ν = 0.2 ACI 318 (Art 116R-45)
ν = 0.2 CEB-FIP (Art 2.1.4.3)
ν = 0.2 EHE (Art 39.9)
ν = 0.2 BS 8110 (Art 2.4.2.4)
ν = 0.2 Australian Standard 3600
ν = 0.2 GB 50010
ν = 0.2 NBR 6118
ν = 0.2 AASHTO Standard Specifications for H. B.
ν = 0.2 Indian Standard 456
ν = 0.2 Cπ 52-101-03
ν = 0.2 ITER Structural Design Code for Buildings
|
|
ρ
|
Density
|
|
Act. time
|
Activation time
|
|
Deact. time
|
Deactivation time
|
|
G
|
Shear modulus. Is calculated using the formula:
|
|
α
|
Coefficient of linear thermal expansion
Default value depends on the active code:
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) Eurocode 2 (Art 3.1.2.5.4)
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) ACI 318 (Art 116R-45)
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) CEB-FIP (Art 2.1.8.3)
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) EHE (Art 39.10)
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) BS 8110 (Part 2: 7.5)
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) Australian Standard 3600
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) GB 50010
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) NBR 6118
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) AASHTO Standard Spec. for H. B.
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) Indian Standard 456
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) Cπ 52-101-03
α = 1.0E-5 (ºC-1) ITER Structural Design Code for Buildings
|
|
Damping
|
Damping properties
|
|
Concrete Specific Properties
| |
|
Ex Type
|
Type of elastic modulus used for linear analysis:
|
|
Linear Ex
|
Modulus of elasticity for linear analysis. The different options for the elastic modulus will vary depending on the active code:
Eurocode 2
Linear Ex = Ecm (default), Ec, Ecd
ACI 318
Linear Ex = Ec (default)
CEB-FIP
Linear Ex = Ec (default), Eci, Ec1
EHE
Linear Ex = Ej (default), Eci, Ec0
BS 8110
Linear Ex = Ec (default)
Australian Standard 3600
Linear Ex = Ec (default)
GB 50010
Linear Ex = Ec (default)
NBR 6118
Linear Ex = Ecs (default), Eci
AASHTO Standard Spec. for H. B.
Linear Ex = Ec (default)
Indian Standard 456
Linear Ex = Ec (default)
Cπ 52-101-03
Linear Ex = Eb (default)
ITER Structural Design Code for Buildings
Linear Ex = Ecm (default), Ec, Ecd
|
|
Ages
|
Ages defined for the concrete time dependent properties (maximum of 20 age values).
Default values:
1, 3, 7, 10, 14, 21, 28, 40, 60, 75, 90, 120, 200, 365, 600, 1000, 1800, 3000, 6000, 10000 days
|
|
Analysis σ-ε diagram
|
Analysis stress-strain diagram. Each different type of stress-strain diagrams available depends on the code for which the material was defined. Apart from available diagrams supported by the codes, it is possible to define new diagrams by changing the table data.
SAε: Strain values corresponding to a point of the diagram.
SAσ: Stress values corresponding to a point of the diagram.
|
|
Design σ-ε diagram
|
Design stress-strain diagram. Each different type of stress-strain diagrams available depends on the code for which the material was defined. Apart from available diagrams supported by the codes, it is possible to define new diagrams by changing the table data.
SDε: Strain values corresponding to a point of the diagram.
SDσ: Stress values corresponding to a point of the diagram.
|
|
ε min
|
Maximum admissible strain in compression at any point of the section (Point B of the pivots diagram)
Sign criterion: + Tension, - Compression
Eurocode 2
ε min = - 0.0035
If concrete has fck > 50 MPa, then
ε min = -(2.6+35[(90-fck)/100]4) · 10-3 (fck in MPa)
ACI 318
ε min = - 0.0030
CEB-FIP
Maximum admissible strains depend on the selected stress-strain diagram:
ε min = - 0.0035 (User defined σ-ε diagram)
ε min = - ε cuB (Parabolic rectangular σ-ε diagram)
ε min = - ε cuU (Uniform stress σ-ε diagram)
EHE
ε min = - 0.0035
If concrete has fck > 50 MPa, then
ε min = -(2.6+14.4[(100-fck)/100]4) · 10-3 (fck in MPa)
BS 8110
ε min = - 0.0035
GB 50010
ε min = ε cu
NBR 6118
ε min = - 0.0035
Indian Standard 456
ε min = - 0.0035
Cπ 52-101-03
ε min = ε b2
|
|
ε int
|
Maximum allowable strain in compression at internal points of the section (Point C of the pivot diagram)
Sign criterion: + Tension, - Compression
Eurocode 2
ε int = - 0.0020
If concrete has fck > 50 MPa, then
ε int = -(2.0+0.085(fck-50)0.53) · 10-3 (fck in MPa)
ACI 318
ε int = 0 (No limit)
CEB-FIP
Maximum admissible strains depend on the selected stress-strain diagram
ε int = - 0.0020 (User defined σ-ε diagram)
ε int = - ε cuC (Parabolic rectangular σ-ε diagram)
ε int = 0 (No limit)
EHE
ε int = - 0.0020
If concrete has fck > 50 MPa, then
ε int = -(2.0+0.085(fck-50)0.5) · 10-3 (fck in MPa)
BS 8110
ε int = 0 (No limit)
GB 50010
ε int = ε 0
NBR 6118
ε int = - 0.0020
Indian Standard 456
ε int = - 0.0020
Cπ 52-101-03
ε int = ε b0
|
|
PCLevel
|
Ratio of the height of the section from the most compressed face at which point C is located:
PCLevel = 3/7 (default value)
|
|
Concrete σ-ε diagrams
| ||
|
Codes
|
Analysis σ-ε diagram
|
Design σ-ε diagram
|
|
EC2_08, EC2_91, ITER, EHE-98 y EHE-08, CEB-FIP
|
Short term loads
|
Parabolic-rectangular
Bilinear
|
|
BS8110
|
Structural Analysis
|
Parabolic-rectangular
|
|
NBR6118
|
|
Parabolic-rectangular
|
|
IS456
|
|
Parabolic-rectangular
|
|
GB50010
|
Structural Analysis
|
Parabolic-rectangular
|
|
Cπ 52101
|
Bilinear
Trilinear
|
Bilinear
Trilinear
|
|
ACI318, ACI349, ACI359, AS3600 and AASHTOHB
|
Parabolic-rectangular
|
Parabolic-rectangular
|
|
Eurocode 2 Concrete Properties
| |
|
βcc
|
Coefficient which depends on concrete age. Used to calculate time-dependant properties:
βcc = exp {s·[1-(28/Age)1/2]} (Age in days)
|
|
γc
|
Partial safety factor. γc = 1.5 (default value)
|
|
εc1
|
Strain of the peak compressive stress. Default values:
εc1= -0.0022 for Eurocode 2 1991 and fck 50MPa
εc1= 0.7·fcm0.31 < 2.8 for Eurocode 2 2008 (- Compression)
|
|
εcu
|
Ultimate strain in compression (- Compression)
|
|
fck
|
Characteristic compressive strength. Depends on concrete age:
fck_t = fcm_t - 8 (fck_t and fcm in MPa) (+ Compression)
|
|
fcd
|
Design compressive strength. Depends on concrete age:
fcd_t = fck_t/ γc (+ Compression)
|
|
fcm
|
Mean compressive strength. Depends on concrete age:
fcm_t = βcc *fcm_28-day (+ Compression)
|
|
fctm
|
Mean tensile strength: (+ Tension)
fctm = 0.3· (fck_28-day 2/3) if fck 50 Mpa (fctm, fcm and fctk in MPa)
fctm = 2.12·ln(1+(fcm_28-day /10)) if fck > 50 MPa
|
|
fctk005
|
Lower characteristic tensile strength (percentile-5%)
fctk005 = 0.7·fctm (+Tension)
|
|
fctk095
|
Upper characteristic tensile strength (percentile-95%)
fctk095 = 1.3·fctm (+Tension)
|
|
Ecm
|
Secant modulus of elasticity. Depends on concrete age:
Ecm = 9500· [(fck_t+8)1/3] (fck_t and Ecm in MPa)
|
|
Ec
|
Tangent modulus of elasticity. Depends on concrete age:
Ec = 1.05·Ecm
|
|
Ecd
|
Design modulus of elasticity. Depends on concrete age:
Ecd = Ecm/ γc
|
|
Cement type
|
Refers to the different types of cement used:
S: Slow hardening cements
N: Slow hardening cements (Default value)
R: Rapid hardening cements
RS: Rapid hardening high strength cements
|
|
ACI 318-05 Concrete Properties
| |||||||||
|
fc
|
Characteristic compressive strength (ACI-209R-4 Art. 2.2.1)
Depends on concrete age:
fc_t = Age / (a+ ß1·Age) ·fc_28-day (+ Compression)
| ||||||||
|
fr
|
Modulus of rupture (ACI-318 Art. 9.5.2.3). Depends on concrete age:
fr·7.5*fc_t1/2
| ||||||||
|
Ec
|
Elastic modulus (Art. 8.5.1 of the ACI-318). Depends on concrete age:
Ec = Wc1.5·33·fc_t1/2 / Wc 155 (Wc in lb/ft3)
| ||||||||
|
Cement type
|
Cement type:
I: cement type I (default value)
III: cement type III
| ||||||||
|
Curing type
|
Curing type:
MOIST: moist cured (default value)
STEAM: steam cured
| ||||||||
|
ß1
|
Factor to transform the parabolic stress distribution of the beam compressive zone to a rectangular one (Art. 10.2.7.3 of the ACI-318). This factor 1 varies depending on the concrete characteristic strength. The different values this factor may have are described below:
Note: All these formulae are valid for fc of 28 days.
| ||||||||
|
0
|
Strain of the peak compressive stress for parabolic stress-strain diagram. (Parabolic Stress strain diagram provided by PCA).
0= 2· (0.85·fc_t)/Ec (+ Compression)
| ||||||||
|
CEB-FIP Concrete Properties
| |||||||||
|
βcc
|
Coefficient which depends on concrete age (Art. 2.1.6.1 (2.1-54))
Used to calculate time-dependant properties:
βcc = exp {s· [1-(28/Age)1/2]} (Age is expressed in days)
| ||||||||
|
γc
|
Partial safety factor. (Art. 1.6.4.4)
γc =1.5 (default value) (c 1)
| ||||||||
|
fck
|
Characteristic compressive strength (Art. 2.1.3.2)
Depends on concrete age:
fck_t = fcm_t - 8 (in MPa) (+Compression)
| ||||||||
|
fcd
|
Design compressive strength (Art. 1.4.1 b)
Depends on concrete age:
fcd_t = fck_t/γc (+Compression)
| ||||||||
|
fcd1
|
Uniform strength for uncracked regions (Art. 6.2.2.2)
Depends on concrete age:
fcd1 = 0.85· (1-fck_t/250) ·fcd_t (fcd1, fck_t and fcd_t in N/mm2)
| ||||||||
|
fcd2
|
Uniform strength for cracked regions (Art. 6.2.2.2)
Depends on concrete age:
fcd2 = 0.60 · (1-fck_t/250) ·fcd_t (fcd2, fck_t and fcd_t in N/mm2)
| ||||||||
|
fcm
|
Mean compressive strength (Art. 2.1.6.1 (2.1-53))
Depends on concrete age:
fcm_t = βcc · fcm_28-day (+Compression)
| ||||||||
|
fctm
|
Mean tensile strength (Art. 2.1.3.3.1 (2.1-4))
fctm = 1.40 · [(fck/10)2/3] (fctm and fck in N/mm2) (+ Tension)
| ||||||||
|
fctk min
|
Lower characteristic tensile strength (Art. 2.1.3.3.1 (2.1-2))
fctk_min = 0.95 · [(fck/10)2/3] (fctk_min and fck in N/mm2) (+ Tension)
| ||||||||
|
fctk max
|
Upper characteristic tensile strength (Art. 2.1.3.3.1 (2.1-3))
fctk_max = 1.85 · [(fck/10)2/3] (fctk_max and fck in N/mm2) (+ Tension)
| ||||||||
|
Cement type
|
Type of cement (appendix d.4.2.1)
| ||||||||
|
εc1
|
Strain of the peak compressive stress (Art. 2.1.4.4.1)
εc1 = - 0.0022 (-Compression)
| ||||||||
|
εcuB
|
Maximum strain in bending for parabolic rectangular diagram (Art. 6.2.2.2 (6.2-2)). This strain varies with the concrete characteristic strength, following the criteria specified bellow: (+ Compression)
| ||||||||
|
εcuC
|
Maximum strain in compression for parabolic rectangular diagram (Art. 6.2.2.2 (6.2-6))
εcuC = 0.0035 (+ Compression)
| ||||||||
|
εcuU
|
Maximum strain for uniform stress diagram (Art. 6.2.2.2 (6.2-6))
εcuU = 0.004 - 0.002· (fck/100) (in N/mm2) (+Compression)
| ||||||||
|
εc lim.
|
Maximum strain in compression (Art. 2.1.4.4.1)
 | ||||||||
|
Eci
|
Tangent modulus of elasticity (Art. 2.1.4.2)
Depends on concrete age:
Eci = βcc1/2· 2.15E4 · {[(fcm_t)/10]1/3} (in N/mm2)
| ||||||||
|
Ec
|
Reduced modulus of elasticity (Art. 2.1.4.2)
Depends on concrete age:
Ec = 0.85 · Eci
| ||||||||
|
Ec1
|
Secant modulus of elasticity (Art. 2.1.4.4.1)
Depends on concrete age:
Ec1 = βcc1/2 ·fcm_t/(- εc1)
| ||||||||
|
EHE Concrete Properties
| |||||||
|
γc
|
Partial safety factor (Art. 15.3)
γc =1.5 (default value) (c 1)
| ||||||
|
βc
|
Coefficient which depends on concrete age (Art. 30.4)
Used to calculate time-dependant properties:
βc = exp {K · [1-(28/Age)1/2]} (Age is expressed in days)
| ||||||
|
K
|
Coefficient (0 K 1) which depends on the type of cement used. The value of this factor can be found in Annex 13 of the EHE-1998 and in 31.3 in the EHE-2008, which states the following:
| ||||||
|
Cement type
|
Type of cement. The different types of cement are described in article Art. 30.4 and are the following:
| ||||||
|
fck
|
Characteristic compressive strength (Art. 39.6)
Depends on concrete age:
fck_j = fck · βc (N/mm2) (+Compression)
| ||||||
|
fcm
|
Mean compressive strength (Art. 39.6)
Depends on concrete age:
fcm_j = fck_j + 8 (N/mm2) (+Compression)
| ||||||
|
fcd
|
Design compressive strength (Art. 39.4)
Depends on concrete age:
fcd_t = fck_t/γc (+Compression)
| ||||||
|
ßt
|
Coefficient which depends on concrete age. Used to calculate time-dependant properties (Art. 30.4)
βt= exp {0.10 · [1-(28/Age)]} (Age is expressed in days)
| ||||||
|
fctm
|
Mean tensile strength (Art. 30.4)
Depends on concrete age:
fctm_j = fctm · βt
fctm = 0.3 · (fck2/3) (N/mm2)
| ||||||
|
fctk005
|
Lower characteristic tensile strength (percentile-5%) (Art. 39.1)
fctk_005 = 0.21· (fck2/3) (N/mm2) (+ Tension)
| ||||||
|
fctk095
|
Upper characteristic tensile strength (percentile-95%) (Art. 39.1)
fctk_095 = 0.39 · ( fck2/3) (N/mm2) (+ Tension)
| ||||||
|
εc1
|
Strain of the peak compressive stress (Art. 21.3.3)
εc1= 0.0022 (default value) (+ Compression)
| ||||||
|
εc lim.
|
Ultimate strain in compression (Art. 21.3.3 Table 21.3.3)
εc lim 0
According to CEB-FIP, Art. 2.1.4.4.1:
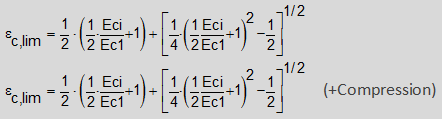 | ||||||
|
Eci
|
Tangent modulus of elasticity (Art. 21.3.3 Table 21.3.3) (Eci 0)
According to the Art. 2.1.4.4.1 of the CEB-FIP code
Eci=2.15· ((fcm/10)1/3) (in MPa)
| ||||||
|
E
|
Secant modulus of elasticity (Art. 39.6)
Depends on concrete age:
Ej = βc1/2 · 8500 · (fcm_j1/3) (N/mm2)
| ||||||
|
E0
|
Initial modulus of elasticity (Art. 39.6)
Depends on concrete age:
E0 = βc1/2 ·10000 · (fcm_j1/3) (N/mm2)
| ||||||